HIT
Assimilator (90 capsules)
A natural product based on herbal enzymes to improve digestion and strengthen immunity. Read more...
In order to find out the price of the product “Assimilator”, contact advisor Leonid Matvijenko in the most convenient way. He/she will provide the price, tell you about the product and how to buy in Canada with a 20% discount on the official website of the Coral Club company.

If assimilation of food is needed more than usual, it is necessary to improve the digestive capacity of the gastrointestinal tract by increasing the amount of digestive enzymes. This is a group of specialized enzymes that break down complex food substances in the gastrointestinal tract into simpler ones, which are then absorbed by the intestinal mucosa and enter the bloodstream. With too little energy for the breakdown of nutrients, as well as insufficient production of enzymes by the gastrointestinal tract itself, it becomes necessary to supplement it from the outside with biologically active food additives, for example with "Assimilator", a natural product that improves digestion. It contains the most important enzymes of plant origin.
 Enzymes that break down carbohydrates.
Enzymes that break down carbohydrates.
 Amylase, the main enzyme of saliva, starts the process of digestion of carbohydrate-rich foods (baked products, cereals, potatoes) in the mouth.
Amylase, the main enzyme of saliva, starts the process of digestion of carbohydrate-rich foods (baked products, cereals, potatoes) in the mouth.
 Cellulase is an enzyme not synthesized by the human digestive system necessary for the digestion of plant fibers (cellulose). Actively breaks down cellulose (fibres) to form glucose. Cellulase improves the nutritional value of grains, fruits and vegetables.
Cellulase is an enzyme not synthesized by the human digestive system necessary for the digestion of plant fibers (cellulose). Actively breaks down cellulose (fibres) to form glucose. Cellulase improves the nutritional value of grains, fruits and vegetables.
 Lactase is an enzyme that breaks down lactose (milk sugar) into glucose. Improves the absorption of dairy products.
Lactase is an enzyme that breaks down lactose (milk sugar) into glucose. Improves the absorption of dairy products.
 Protease, together with other enzymes - papain and bromelain - promote the breakdown of proteins into simple amino acids, improving the quality of their assimilation. This prevents the deposition of protein residues on the intestinal wall and improves protein metabolism. Protease also promotes the destruction of proteinaceous pathogens, strengthening the body's immune system.
Protease, together with other enzymes - papain and bromelain - promote the breakdown of proteins into simple amino acids, improving the quality of their assimilation. This prevents the deposition of protein residues on the intestinal wall and improves protein metabolism. Protease also promotes the destruction of proteinaceous pathogens, strengthening the body's immune system.
 Papain and Bromelain are active in both acidic and alkaline environments of the digestive tract, breaking down proteins to a state where they can be easily absorbed.
Papain and Bromelain are active in both acidic and alkaline environments of the digestive tract, breaking down proteins to a state where they can be easily absorbed.
 Lipase, active in the small intestine, breaks down the saturated fats of animal foods (meat, dairy and seafood), converts them into easily digestible fatty acids, aids the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A and D.
Lipase, active in the small intestine, breaks down the saturated fats of animal foods (meat, dairy and seafood), converts them into easily digestible fatty acids, aids the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A and D.
 Vitamin A is an antioxidant, strengthens resistance to infections, plays an important role in cellular immunity, contributes to the metabolism of fats, protects the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Vitamin A is an antioxidant, strengthens resistance to infections, plays an important role in cellular immunity, contributes to the metabolism of fats, protects the gastrointestinal mucosa.
 Vitamin D regulates calcium-phosphorus metabolism and increases the permeability of the intestinal walls for better absorption of nutrients in the digestive tract.
Vitamin D regulates calcium-phosphorus metabolism and increases the permeability of the intestinal walls for better absorption of nutrients in the digestive tract.
 Improving digestion and absorption of food.
Improving digestion and absorption of food.
 Stops flatulence, heaviness in the stomach.
Stops flatulence, heaviness in the stomach.
 Provides cells with nutrients.
Provides cells with nutrients.
 Increases the body's immune status.
Increases the body's immune status.
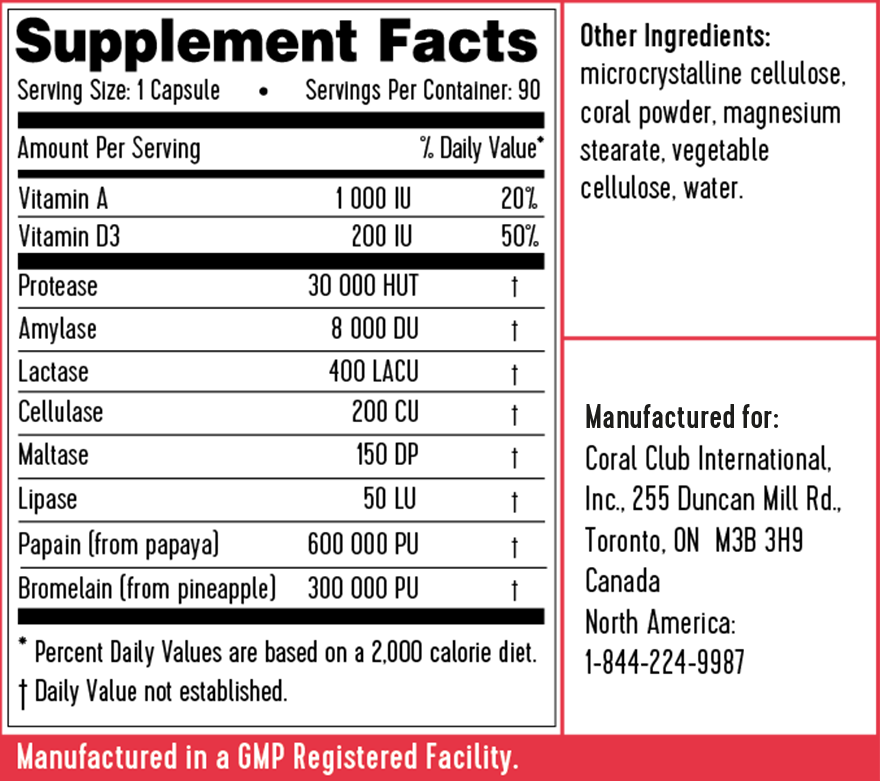
 Protease 30,000 units
Protease 30,000 units
 Amylase 8000 units
Amylase 8000 units
 Lipase 50 units
Lipase 50 units
 Maltaza 150 units
Maltaza 150 units
 Lactase 400 units
Lactase 400 units
 Cellulase 200 units
Cellulase 200 units
 Papain 600,000 units
Papain 600,000 units
 Bromelain 300,000 units
Bromelain 300,000 units
 Vitamin A 1000 IU
Vitamin A 1000 IU
 Vitamin D3 200 IU
Vitamin D3 200 IU
 Auxiliary Components
Auxiliary Components
EFFECT OF THE ACTIVE COMPONENTS
ENZYMES, DEGRADING PROTEINS
FAT-BREAKING ENZYMES
APPLICATION
INGREDIENTS
YOUR CORAL CLUB CONSULTANT